Medically Reviewed by Dr. Lisa Hartford, MD
Skin is among the largest organs in the body. It has the ability to stretch and go back to its original shape. In addition, it has functions such as thermal regulation, protection, and maintaining hydration in the body.
What keeps the skin elastic yet firm is collagen inside it. Collagen is the structural element of the skin that keeps it elastic and in shape. Just like any other function in the body, collagen is generated in the cells. It is at its prime at a young age as compared to older skin.
Aging signs such as wrinkles and sagginess appear as the skin gets older. This may also be accompanied by skin thinning and increasing laxity. Many people turn to therapies that may rejuvenate collagen in the skin without being too invasive. Radiofrequency therapy with thermal impact is one effective way of supporting neocollagenesis. Keep reading to learn more about getting younger-looking skin with RF facials.
What is Skin Laxity?
Human skin ages with time due to several external and internal factors. These may include sun exposure, genetics, environmental pollution, gravity, diet, lifestyle, and lack of skincare. This causes the skin to sag and become loose. The loss of structural integrity and firmness of the skin is called skin laxity.
Early aging signs related to skin laxity may include saggy jowls, lines around the mouth, and loss of jawline definition. Sudden weight loss or change may also trigger sagginess in the skin. Sun exposure is a primary reason for skin laxity due to harsh UV rays. This includes wrinkles, vascular disorders, and sagging skin.

A recent study with 298 women aged between 30 and 78 concluded sun exposure caused saggy skin. It was determined that 80% of their facial aging was due to the sun's UV rays. The rays are potent enough to cause collagen and elastin breakdown over time. Moreover, exposure to the sun leads to epidermis thinning and making the wrinkles look more visible.
Skin becoming laxative is a gradual process; however, it may start in the twenties and thirties. The sag may occur at a rate of 1% per year, which may become more pronounced by the time you reach your 40s. This is when you may start to notice deep lines and age spots on your face and neck.
Impact of Collagen on Skin
Collagen is a protein that's present in the skin that acts as a primary building block. It gives structural integrity to the skin, muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Collagen is among the most abundant proteins in the body that also helps in regeneration when there is a wound or impact.
Skin collagen ensures it stays stretchy and elastic so that it can move and bounce back as needed. Additionally, collagen regenerates the skin to prevent early wrinkling and roughness.
However, aging, sun damage, lifestyle, and genetics lead to the breakdown of the collagen protein. When collagen starts to harden due to cross-linking, it is unable to bounce back to its original form.
This leads to fine lines, wrinkles, and skin sagging. More collagen in the skin is a sign of good health and rejuvenation power. The decline in collagen starts to appear on the skin as skin laxity, thinning, and a tendency to get damaged easily.
Understanding Neocollagenesis
As discussed, collagen formation and regeneration of the skin keep it healthy and elastic. The human body replenishes collagen with the help of fibroblast activity in the cells. Due to the stretching of the skin, fibroblast cells are able to get into action and start attaching to a protein matrix with integrin receptors.
With the help of ongoing neocollagenesis, the body generates new collagen, which serves as a crucial structural protein for the skin, tendons, ligaments, and various other connective tissues. Collagen helps in maintaining the skin's firmness, elasticity, and youthful appearance.
As we age, our body's ability to produce collagen decreases, leading to the gradual loss of skin elasticity and the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging. By the time we reach our 30s, collagen production begins to decline significantly, contributing to the visible signs of aging.
From a skincare and rejuvenation point of view, neocollagenesis is a fascinating concept. It involves stimulating the body to create fresh collagen for wound healing and replenishing skin health. Various treatments and products are designed to promote this process, helping to improve skin texture, reduce the appearance of mild wrinkles, and restore a more youthful look. These treatments may range from non-invasive to invasive.
The duration of neocollagenesis may take 2-3 months. During this time, treatments or interventions work by triggering collagen production within the skin's deeper layers. It's important to note that while neocollagenesis can lead to significant improvements in skin quality, the extent of these improvements may vary from person to person. The natural aging process, genetics, and the specific treatment used can all influence the final results.
Several methods can stimulate neocollagenesis, including radio frequency, dermal heating techniques, red LED therapy, and laser technologies. These methods have been shown to be particularly effective in increasing collagen production and skin tightening. For those who are looking for skin rejuvenation, these treatments can help individuals maintain or restore a more youthful appearance by addressing collagen loss and promoting the growth of new collagen protein fibers within the skin.
How Does Thermal Energy Support Neocollagenesis
Over the years, the slowing down of collagen production has been studied to develop new effective ways to stimulate it again. Some of these energy-based therapies are radio-frequency (RF), infrared, and deep ultrasound. They generate heat at a cellular level, triggering neocollagenesis. As a result of this, the skin becomes firm, tighter, lifted, and smooth.
Monopolar RF with an electromagnetic field (EMF) and alternating polarity can stimulate the movement of charged particles, releasing an electric current. This current works its way through the hydrophilic structures like dermal collagen framework and underlying fibers.
Tissues resist this flow of current and generate localized heat. This may occur between 60-65°C, leading to collagen generation. Any temperature below 60° will not be effective. As we increase the temperature above 70°, neocollagenesis will improve.

The neocollagenesis mainly occurs in the dermis and upper, mid, and deep reticular dermis. Another phenomenon observed is neoelastinogenesis, which creates elastin in the papillary dermis and upper- and mid-reticular dermis.
Another way to generate neocollagenesis in the mid and deep reticular dermis and neo-elastogenesis in the deep reticular dermis high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) may also be used. In fact, HIFU delivers the highest level of neocollagenesis in comparison to other techniques.
The collagen generation may take over a month with these treatments. In a clinical study, the neocollagenesis was noted at 30 days after the heat treatment. Moreover, skin hydration improved with new hyaluronic acid after ten weeks of the treatment.
Radiofrequency Therapy for Collagen Regeneration
Radiofrequency efficacy was studied in a clinical trial. Six participants with class I to II wrinkles were given RF treatment for 3 months. Before the treatment, the participants were studied to collect biopsies and photographs to compare later. After the treatment of 6 sessions at 2-week intervals, the same information was taken at 3 and 6 months.
In addition to blinded visual comparisons, a computerized quantitative evaluation was done to estimate the elastin, collagen types I and III, and neocollagenesis. Furthermore, immunohistochemical techniques were used for quantifying the results.
The trial concluded RF added a significant improvement to the wrinkles. Overall, facial skin looked and felt rejuvenated when compared to the baseline.
Another clinical trial with 12 biopsies from six participants showed a significant improvement in fibroblast activity, type I and III collagen, and skin elasticity. Hence, neocollagenesis occurred at a faster pace during and after the treatment.
At-Home RF Therapy
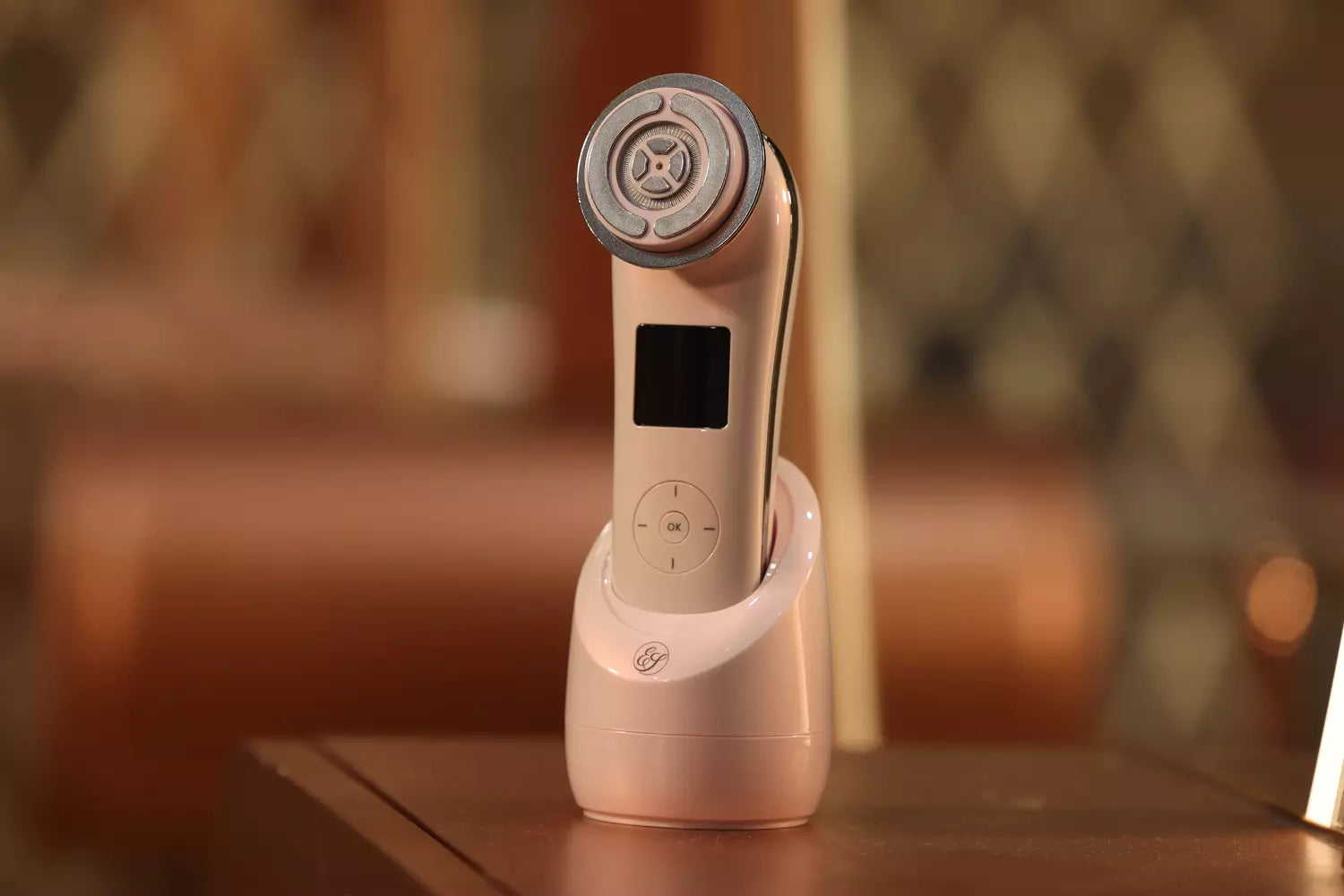
When looking for at-home RF devices, we recommend using the EvenSkyn® Lumo Anti-Aging & Skin Tightening Handset. The device is safe for at-home RF treatment as it is FDA, Health Canada, CE, EMC, and RoHS-compliant. It is a multi-functional device that has five different skin rejuvenating therapies. With Radiofrequency, EMS, and LED light therapy, the Lumo device aids in stimulating collagen and tightening facial muscles.

It may also help with fine line and wrinkle reduction. Additionally, two-tier dermal heating will heat the dermal layer for neocollagenesis. So, you may expect younger-looking skin and even complexion after regular use. To use the device, clean your face and apply conduction gel. Press start, and pick from different settings. You may alternate between the modes as you prefer.
As the Lumo has 5 different modes (with 5 intensity levels), start with the lowest settings and adjust depending on your comfortability and tolerance. Use the device for 15-20 minutes twice or thrice a week.
Wrapping Up
Aging signs such as saggy skin, laxity, wrinkles, and fine lines are inevitable; however, there's a way to delay them and enjoy youthful-looking skin. Thermally heating the skin cells using radiofrequency therapy is one way to generate the depleting collagen in the skin.
RF, when used in tandem with the right skincare and therapies like LED and microcurrent, may give the best results. As neocollagenesis occurs over a month, be patient and maintain consistency.
References:
- Flament F, Bazin R, Laquieze S, Rubert V, Simonpietri E, Piot B. "Effect of the sun on visible clinical signs of aging in Caucasian skin." Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013 Sep
- Mehrabani D, Manafi N. "Role of cultured skin fibroblasts in aesthetic and plastic surgery." World J Plast Surg. 2013 Jan
- Hantash BM, Ubeid AA, Chang H, Kafi R, Renton B. "Bipolar fractional radiofrequency treatment induces neoelastogenesis and neocollagenesis." Lasers Surg Med. 2009 Jan
- Dayan E, Burns AJ, Rohrich RJ, Theodorou S. "The Use of Radiofrequency in Aesthetic Surgery." Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2020 Aug 17
- Magaki S, Hojat SA, Wei B, So A, Yong WH. "An Introduction to the Performance of Immunohistochemistry." Methods Mol Biol. 2019
- Ricard-Blum S. "The collagen family." Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 Jan 1
- el-Domyati M, el-Ammawi TS, Medhat W, Moawad O, Brennan D, Mahoney MG, Uitto J. "Radiofrequency facial rejuvenation: evidence-based effect." J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011 Mar








Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.