Medically Reviewed by Dr. Lisa Hartford, MD
Collagen is the building block for skin and how it appears on the outside. It is a protein that weighs about 30% of your body's dry weight. Collagen has a fibrous structure, and apart from providing elasticity and resilience to the skin and the body organs, it governs cellular shape and behavior.
Collagen is present in the skin's dermis, giving it structure and thickness. Being responsible for skin rejuvenation and healing, it keeps the skin flexible. However, with age, the body synthesizes less collagen protein. This is what leads to the signs of aging.
Good skincare and diet may help to support collagen in the body. Another way to do so is by using microcurrent facials to stimulate collagen. Keep reading to learn more about how microcurrent affects collagen.
What is Collagen?
Collagen is a protein consisting mainly of amino acids (glycine, hydroxyproline, and proline). It's essential to provide structural support to the connective tissues. Collagen can stretch due to its rigidity and resistance. This ensures a strong tissue connects the skin, ligaments, tendons, and bones while allowing movement.
In simple words, collagen is the protein that holds everything together. It's a connective medium that keeps your skin from sagging and ensuring it looks plump. If you consume ample protein-rich food, manganese, zinc, and copper, your body will keep replenishing collagen.
Moreover, good skincare practice also helps in collagen formation. Another factor that impacts collagen production is age. As we get older, the synthesis may decline. Hence, it leads to aging signs like wrinkles, fine lines, age spots, and saggy skin.
Role of Collagen in the Human Body
Collagen is an essential protein providing strength and structure to the cells in the body. About 28 types of collagen have been identified so far. The most common type is type I, mainly in the skin, bones, organs, tendons, cornea, and fascia.

Collagen fibers create elastin and hyaluronic acid in the skin. Elastin keeps the skin tight, and hyaluronic acid is a tissue lubricant.
Here are some more cellular activities aided by collagen:
Adding skin elasticity
Collagen leads to an increase in fibroblasts and extracellular matrix proteins, leading to enhanced elasticity. Fibroblasts further regulate the creation of more protein when there is tension or a wound in the skin. Collagen not only adds elasticity but also decreases metalloproteinase, which is a collagen-breaking enzyme.
Blood clotting and wound healing
Collagen comes into play when there is any impact on the blood vessels. It attracts platelets to form a blood clot and stop the bleeding. With the process of inflammation modulation and angiogenic signals, collagen fragments promote the development of new blood vessels. Collagen scars are usually formed during wound healing due to new fibroblasts in the skin.
Removing and replacing dead skin cells
Collagen helps to form fibroblasts in the dermis, which leads to new cell growth. Skin cells are constantly repaired, removed, and replaced. This process is called mitosis. The skin regeneration process may take about a month for most adults.
Do Microcurrent Facials Trigger Collagen Formation?
In a study of the effect of microcurrents on fibroblasts in the cells, a series of microcurrents was delivered remotely to the cell culture. These affected the mitogen-activated protein kinases. These protein molecules help in cellular functions, such as proliferation and migration.
Moreover, the microcurrent's TGF-β1 release triggered the synthesis of collagen I, III, IV, and fibronectin. All these components aid in the wound healing process and collagen generation.
Microcurrent facials also lead to ATP generation. As the human body works using bioelectric impulses, the microcurrent mimics the body's electrical signals. This leads to an increase in adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
ATP in the cell aids in protein synthesis and muscle contraction. Furthermore, with the help of metabolic processes, ATP produces collagen and elastin in the skin.
At-Home Microcurrent Device for Facial Rejuvenation
Microcurrent therapy is non-invasive as it involves passing a low level of electrical current using a microcurrent device. It is commonly used to improve skin appearance, reduce the mild signs of aging, and promote a more youthful look.

There's some evidence that electrical stimulation may increase collagen and blood flow to the skin. Consistent sessions may lead to a firmer and more radiant complexion. Moreover, it may be one way to work out your facial muscles, ultimately aiming to enhance the contour of the face.
If the thought of electric current passing through your face scares you, know it is a painless process. You won't even feel the microcurrent on your skin! Since the process works at a cellular level, facial rejuvenation may take a few sessions to be visible.
You may visit a professional or invest in an excellent at-home microcurrent device. Using at-home devices will be more affordable and convenient than booking appointments and going to an aesthetician.
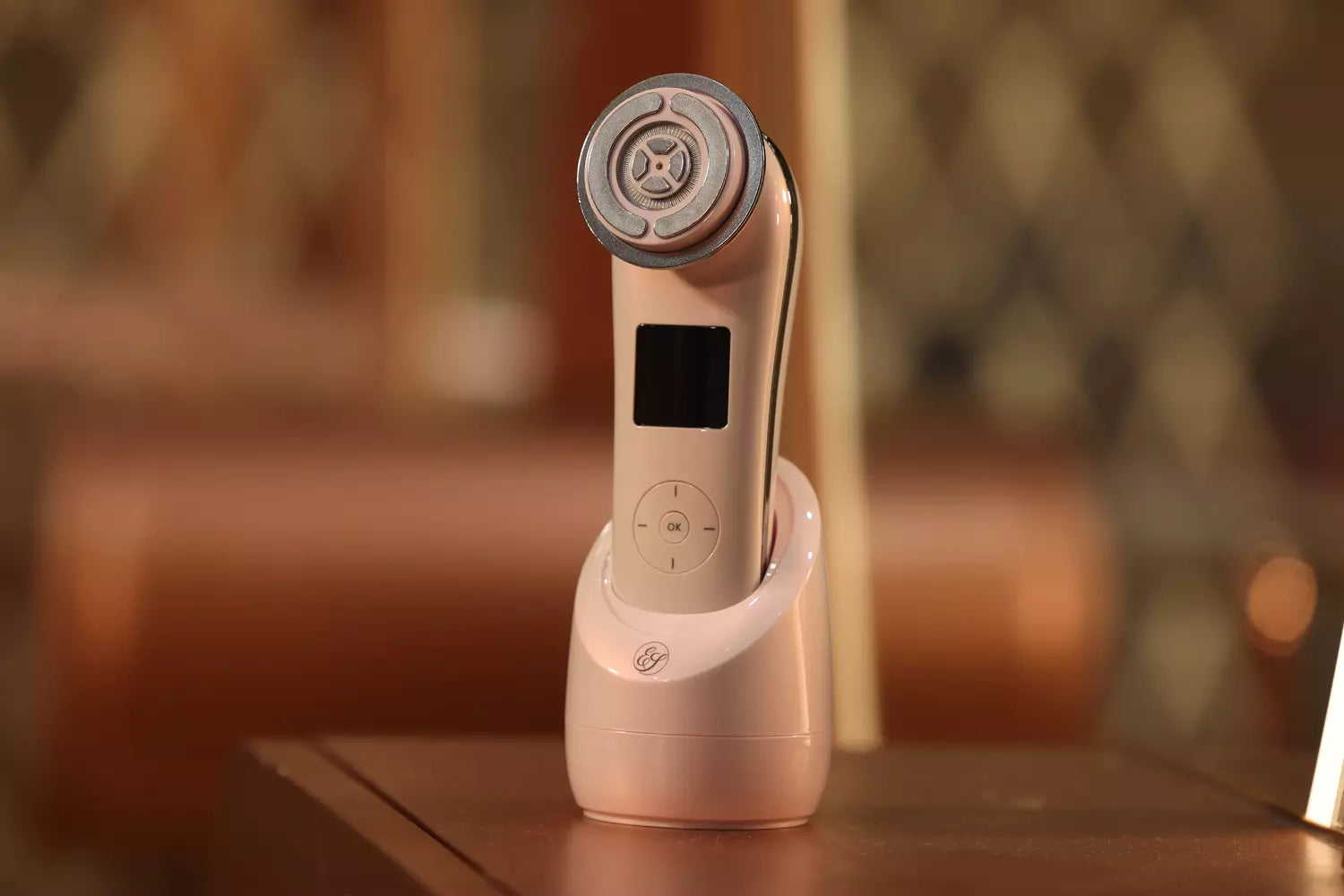
The EvenSkyn® Phoenix: Premium Face Lifting Microcurrent Bar is an easy-to-use device. It combines microcurrent with deep kneading mechanical massaging, and derma rolling. You may use the device on your face & neck massaging for toning and de-puffing.
One of the best features of the device is that it works using natural and artificial light. Implying you never need to charge it! The microcurrent bar has 4 alloy rollers placed at a 115° angle for maximum skin contact and delivering deep tissue massaging action.
Clean your skin and use the roller on the skin for 5 to 10 minutes in a given region. Also, use a conductive gel on the skin for easy gliding and better conductivity of the device current. The EvenSkyn® Conduction gel contains hyaluronic acid and collagen peptides aiding lubrication and hydration.
It's important to note that while microcurrent therapy is generally considered safe for most people, it's always advisable to consult a healthcare professional or licensed esthetician before starting any new beauty treatment. If you perform an at-home facial, always try it on a small patch of skin and follow the device's instructions.
Benefits of Microcurrent Facials
Here's why you should be consistent with microcurrent facials for radiant skin.
- Microcurrents may tone facial muscles, leading to a more lifted and contoured appearance.
- The increase in ATP production may promote the synthesis of collagen and elastin. These are crucial proteins for maintaining skin elasticity and firmness.
- It may enhance blood flow, bringing essential nutrients and oxygen to the skin cells.
- Enhanced increased collagen production may reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and skin texture.
- Microcurrents may stimulate the lymphatic system, helping to reduce puffiness and fluid retention.
- The electrical currents may improve the penetration of skincare products into the skin, making them more effective.
Wrapping Up
Now you know collagen plays a crucial role in maintaining the skin's strength, elasticity, and overall appearance. Aging leads to visible signs of collagen reduction in fine lines and wrinkles. However, you may manage these signs with microcurrent facials.
Microcurrent therapy, whether performed professionally or at home with devices like the EvenSkyn Phoenix, may tone facial muscles, improve blood flow, and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Remember to be consistent with the facial and regular skincare regime for best results. Moreover, eating a balanced diet rich in collagen-supporting nutrients may contribute to a more radiant, youthful complexion and healthier skin in the long run.
References:
J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. "Enigmatic insight into collagen: 2016
Marlyn Wu; Kelly Cronin; Jonathan S. Crane. "Biochemistry, Collagen Synthesis" 2022
National Human Genome Research Institute. "FIBROBLAST" July 18, 2023
Shomita S. Mathew-Steiner, Sashwati Roy, and Chandan K. Sen. "Collagen in Wound Healing" 2021
Ye-Rang Yun, Jong Eun Won, Eunyi Jeon, Sujin Lee. "Fibroblast Growth Factors: Biology, Function, and Application for Tissue Regeneration" 2010
National Human Genome Research Institute. "MITOSIS" July 18, 2023
T A Aleksanyan, E V Kazantsev. "Treatment with the use of microcurrent lymphatic drainage physiotherapy during the postoperative period following rhinoplastic surgery" 2016
Chao Yu, Zong-Qian Hu, Rui-Yun Peng. "Effects and mechanisms of a microcurrent dressing on skin wound healing: a review," 2014
Evangelia Konstantinou, Zoi Zagoriti. "Microcurrent Stimulation Triggers MAPK Signaling and TGF-β1 Release in Fibroblast and Osteoblast-Like Cell Lines" 2020
Charles Kennedy. "Adenosine Triphosphate" 2007
Jack A. Tuszynski. "The Bioelectric Circuitry of the Cell" August 28, 2019.
Alessandro Piras, Lorenzo Zini, Aurelio Trofè. "Effects of Acute Microcurrent Electrical Stimulation on Muscle Function and Subsequent Recovery Strategy" 2021
Lenka Kubiczkova, Lenka Sedlarikova, Roman Hajek & Sabina Sevcikova. "TGF-β – an excellent servant but a bad master" 2012
Michael Schunck, Vivian Zague, Steffen Oesser, and Ehrhardt Proksch. "Dietary Supplementation with Specific Collagen Peptides Has a Body Mass Index-Dependent Beneficial Effect on Cellulite Morphology" 2015
Sylvie Ricard-Blum. “The Collagen Family” 2011








Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.